Sql Server에서 제공하는 SP중 비공식문서에만 존재하는 sp_MSforeachdb 에 몇가지 기능을 추가한 SP를 웹에서 발견하였다.
Problem
While the system procedure sp_MSforeachdb is neither documented nor officially supported, most SQL Server professionals have used it at one time or another. This is typically for ad hoc maintenance tasks, but many people (myself included) have used this type of looping activity in permanent routines. Sadly, I have discovered instances where, under heavy load and/or with a large number of databases, the procedure can actually skip multiple catalogs with no error or warning message. Since this situation is not easily reproducible, and since Microsoft typically has no interest in fixing unsupported objects, this may be happening in your environment right now.
Solution
In my environment, the minute I discovered the issue, I promptly wrote a replacement. (I blogged about my replacement earlier this year.) While I was writing the new stored procedure, it struck me that, while I was making my maintenance processes more reliable, I could also make them more flexible.
For example, I could have the procedure operate only on databases that:
- are system databases (master, msdb, model, tempdb);
- are non-system databases;
- match a specific name pattern;
- are in a comma-separated list of db names;
- have a specific recovery model or compatibility level;
- are read only or have auto-close or auto-shrink enabled; or,
- have service broker enabled.
Some other handy options I thought to add, which aren't in sp_MSforeachdb, include an option to print the database name before each result, or even to only print the command instead of executing. This can be very handy if you are trying to set a slew of databases to SINGLE_USER and don't want the operations to happen serially; you can print the commands and split the output across multiple Management Studio windows.
With all that said, here is the stored procedure in its current form:
■ 소스보기 ↓
Caveats
The procedure doesn't cope well with databases with a single quote ( ' ) in their name or with leading / trailing spaces, but it gladly handles databases that violate other best practices, such as beginning with a number or containing special characters like ., ", [, or ]. Here is a quick list of databases that it has been tested against:
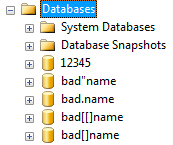
(Try creating those databases on your system and running EXEC sp_MSforeachdb 'SELECT * FROM ?.sys.objects;'; - you'll get a variety of errors.)
Also, you do not need to QUOTENAME parameter values... you should pass in 'master, model' to @database_list, not '[master], [model]', and you should use 'USE ?;' and not 'USE [?];' for the command and replace_character values - this escaping is handled for you. However, if you have a command where you want to be able to selectively choose whether or not to apply QUOTENAME to the replace_character (for example, @command = 'SELECT ''[?]'', * FROM sys.databases WHERE name = ''?'';'), you can use the override parameter @suppress_quotename.
While there are parsing solutions for all of these problems, they quickly explode the code and become more maintenance trouble than they're worth. At least, in this author's opinion.
Finally, the procedure does not currently include any logging or error handling, which you may want to add if you are going to use this type of procedure in any automated processes.
Examples
To perform a full backup to the same folder of all user databases that are in simple mode. This is one case where you'll want to use the @suppress_quotename parameter, otherwise you end up with files named [database_name].bak.
To search all databases matching the name pattern 'Company%' for objects matching the name pattern '%foo%'. Place into a #temp table so the result is a single result set instead of the number of databases that match the naming pattern.
To turn auto_shrink off for all databases where it is enabled:
To find the last created object date/time for each database in a defined set (in this case, three databases that I know exist).
To reset service broker for every database - after testing an application, for example:
Next Steps
- Create your own version of sp_foreachdb in master.
- Add logging and/or error handling according to the standards and conventions in your environment.
- Begin phasing the new procedure into processes where you are currently using sp_MSforeachdb.
- Review the following tips and other resources:
'SQL > 도움말 팁들!' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 대용량 INSERT .. SELECT 작업 중 중지했을 때 대처 방안 (0) | 2011.10.24 |
|---|---|
| 테이블 row count 빠르게 계산하는 방법 (0) | 2011.10.18 |
| SQL Server 2005에서 사용하지 않는 테이블을 찾아 정리하는 방법 (0) | 2011.10.18 |
| DATETIME에서 지원하는 가장 빠른 날짜가 1753년인 이유는? (0) | 2011.09.26 |
| SQL 뭐라고 읽어야 하나.....? 씨퀄? 에스큐엘? (0) | 2011.09.26 |
